Tosan Autonomous Surface Vehicle (ASV)
An undergraduate student project supported by university funding.
Quick Summary
Tosan is a remote-controlled, high-maneuverability catamaran-type surface vehicle developed for the 3rd Autonomous Surface Vehicle (ASV) Competition in Tehran, Iran, in 2014. The project focused on innovative mechanical design (catamaran hull and propulsion) and custom electrical systems (power, steering, and braking) to maximize speed, stability, and control.
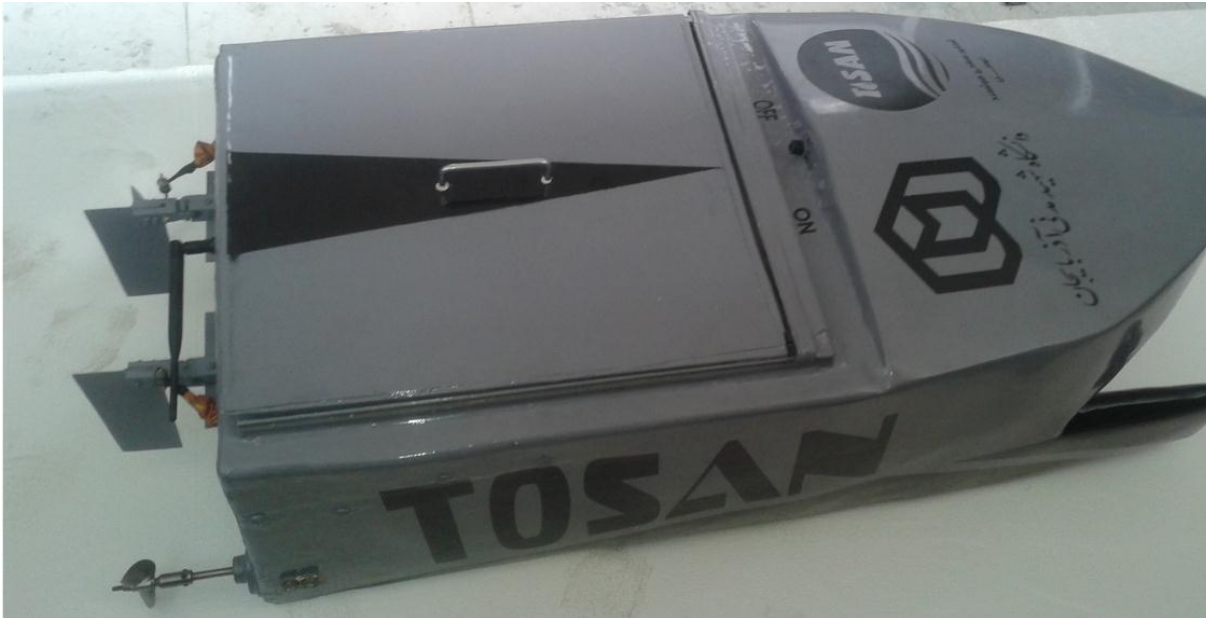

The final design of Tosan.
My Role & Team
- Role: The project was a collaboration between three mechanical engineers and two electrical engineers. As an Electrical Engineer, I was responsible for the custom circuit board design, and motor control logic.
- Duration: The project was initiated in 2012 and concluded after participating in the national competition in 2014.
Key Technologies & Components
- Processor: AVR ATmega32
- Programming Language: BASIC (initial development in C)
- Design Software: Proteus Design Suite (for schematics and PCBs)
- Motors: Two high-efficiency brushless motors (for thrust) and two servo motors (for steering).
- Power: Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) battery (six-cell 5000mAh 22.2v).
- Hull Material: Glass epoxy resin composite (selected for light weight and high maneuverability).
- Control System: controlled via an 11-Channel 2.4GHz radio remote control.
Technical Problem & Solution
- High-Speed Stability and Maneuverability
- Problem: Designing a vessel that could maintain stability at speed while having a shallow draft and high turning capacity for competition requirements.
- Solution (Mechanical Design): We utilized a catamaran hull design (two parallel hulls). This geometry provides stability through a wide beam, reduces hull volume and displacement, and increases overall maneuverability compared to mono-hulls.
- Coordinated Propulsion and Steering
- Problem: Achieving the tightest possible turns at higher speeds for optimized course navigation.
- Solution (Coordinated Control System): Steering utilized two rudders controlled by servo motors, but performance was enhanced by coordinating the thrust. To turn, for example, the rudders move right, and simultaneously, the right-side motor speed is decreased. This coordinated propeller and rudder action enabled tighter turns with a lower radius.
- Rapid Emergency Braking System
- Problem: Safely and quickly bringing the vehicle to a complete halt.
- Solution (Two-Step Braking Logic): A custom two-step braking process was implemented. First, both thrust motors are immediately turned off. Second, the rudders are moved to opposite directions (one left, one right) to create maximum drag and halt the vehicle in the shortest possible time.
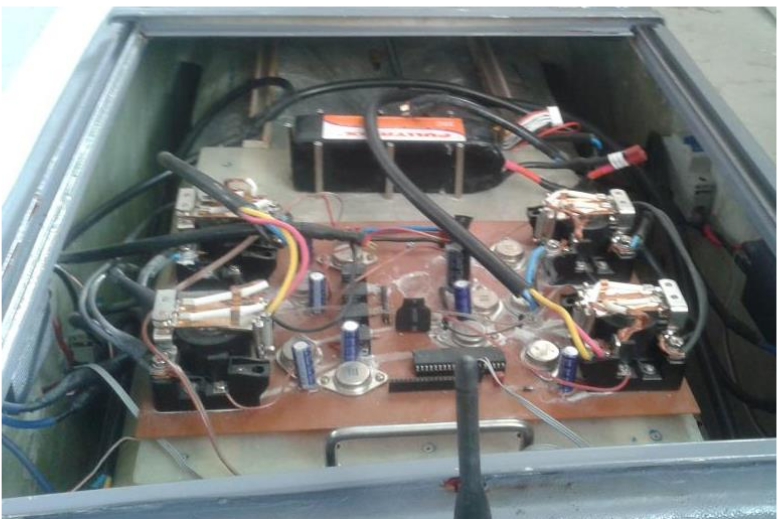
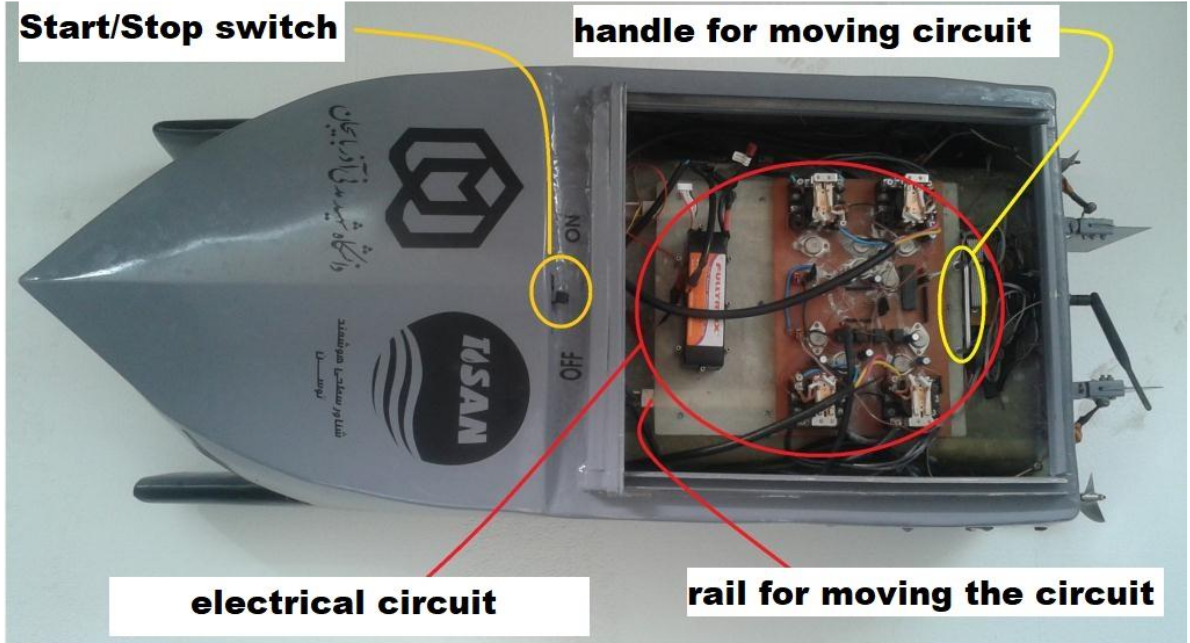

Tosan's electrical circuite board.
Achievements & Outcome
- Primary Goal: Successfully designed, built, and tested the Tosan surface vehicle for the 3rd Autonomous Surface Vehicle (ASV) Competition.
- Recognition: The project earned the admirable prize at the 6th Harkat national festival in Tehran, Iran.
Links
For more information, please read the Technical Report.